Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how about SQL MINUS operator and how to simulate MINUS in MySQL using join.
Please note that MySQL supported the EXCEPT operator starting from version 8.0.31. The EXCEPT operator is equivalent to the MINUS operator. If you are using a lower version, you can refer to this tutorial to emulate the MINUS operator.
Introduction to SQL MINUS operator
The MINUS operator is one of three set operators in the SQL standard that includes UNION, INTERSECT, and MINUS.
The MINUS compares the results of two queries and returns the rows from the result set of the first query that does not appear in the result set of the second query.
The following illustrates the syntax of the MINUS operator:
SELECT select_list1
FROM table_name1
MINUS
SELECT select_list2
FROM table_name2;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The basic rules for queries that use the MINUS operator are the following:
- The number and order of columns in both
select_list1andselect_list2must be the same. - The data types of the corresponding columns in both queries must be compatible.
Suppose that we have two tables t1 and t2 with the following structure and data:
CREATE TABLE t1 (
id INT PRIMARY KEY
);
CREATE TABLE t2 (
id INT PRIMARY KEY
);
INSERT INTO t1 VALUES (1),(2),(3);
INSERT INTO t2 VALUES (2),(3),(4);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following query returns distinct values from the query of the t1 table that is not found in the result of the query of the t2 table.
SELECT id FROM t1
MINUS
SELECT id FROM t2; Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)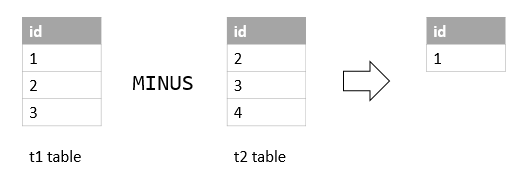
The following Venn diagram illustrates the MINUS operation:
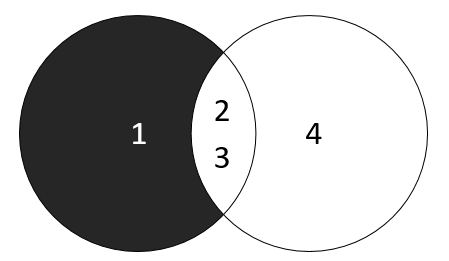
Unfortunately, MySQL does not support MINUS operator in the before version 8.0.31. However, you can use join to emulate it.
MySQL MINUS operator emulation
To emulate the MINUS of two queries, you use the following syntax:
SELECT
select_list
FROM
table1
LEFT JOIN table2
ON join_predicate
WHERE
table2.column_name IS NULL; Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)For example, the following query uses the LEFT JOIN clause to return the same result as the MINUS operator:
SELECT
id
FROM
t1
LEFT JOIN
t2 USING (id)
WHERE
t2.id IS NULL;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this tutorial, you have learned about the SQL MINUS operator and how to emulate the MINUS operator in MySQL using LEFT JOIN clause.